 [C언어] 실습: 헤더 파일 및 C 파일 만들기
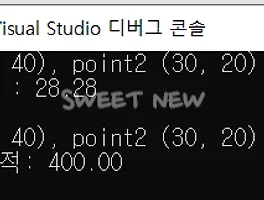
헤더 파일 및 C 파일 만들기 1. main.c #include #include"point.h" #include"line.h" #include"rect.h" double distance(Line *pLine); double area(Rect *pRect); int main(){ Line l1 = {{10, 40}, {30, 20}}; Rect r1 = {{10, 40}, {30, 20}}; printf("point1 (%d, %d), point2 (%d, %d)\n", l1.start.x, l1.start.y, l1.end.x, l1.end.y); printf("직선의 길이 : %.2lf\n\n", distance(&l1)); printf("point1 (%d, %d), point2 (%d, %d)\n"..
[C언어] 실습: 헤더 파일 및 C 파일 만들기
헤더 파일 및 C 파일 만들기 1. main.c #include #include"point.h" #include"line.h" #include"rect.h" double distance(Line *pLine); double area(Rect *pRect); int main(){ Line l1 = {{10, 40}, {30, 20}}; Rect r1 = {{10, 40}, {30, 20}}; printf("point1 (%d, %d), point2 (%d, %d)\n", l1.start.x, l1.start.y, l1.end.x, l1.end.y); printf("직선의 길이 : %.2lf\n\n", distance(&l1)); printf("point1 (%d, %d), point2 (%d, %d)\n"..